How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision surveying. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced flight techniques and legal considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of different drone types, flight modes, and camera settings, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your existing skills, this guide offers a structured approach to mastering drone operation. We’ll delve into the importance of safety procedures, legal compliance, and effective battery management, ensuring you operate your drone responsibly and within the relevant regulations. Get ready to embark on a journey of aerial exploration!
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight check is paramount to ensure both safety and operational success. Neglecting this crucial step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and legal repercussions. This section Artikels a comprehensive checklist and step-by-step procedure for a safe pre-flight inspection.
Pre-Flight Checklist

A comprehensive pre-flight checklist ensures all systems are functioning correctly and the environment is suitable for flight. This includes verifying battery levels, GPS signal strength, and assessing weather conditions. Ignoring any of these aspects can compromise flight safety.
| Check Item | Procedure | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check the battery indicator on the drone and remote controller. | Battery level above 80% | Battery level below 80%; replace or recharge battery. |
| GPS Signal Strength | Observe the GPS signal indicator on the remote controller. Ensure sufficient satellites are acquired. | Strong, stable GPS signal with at least 6 satellites. | Weak or unstable GPS signal; find a location with better reception or postpone flight. |
| Weather Conditions | Check the wind speed, precipitation, and visibility. | Wind speed below 20 mph (32 km/h), no precipitation, good visibility. | High wind speeds, precipitation, or poor visibility; postpone flight. |
| Propeller Integrity | Visually inspect each propeller for damage or cracks. | All propellers are undamaged and securely attached. | Damaged or loose propellers; replace damaged propellers and ensure secure attachment. |
| Gimbal Functionality | If equipped, check the gimbal’s movement and stability. | Gimbal moves smoothly and locks securely in place. | Gimbal is malfunctioning; troubleshoot or postpone flight. |
Pre-Flight Inspection Procedure
- Power on the remote controller and drone.
- Check battery levels and ensure sufficient charge.
- Verify GPS signal strength and wait for sufficient satellite acquisition.
- Assess weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Visually inspect the drone for any damage, loose parts, or obstructions.
- Calibrate the compass if necessary (consult your drone’s manual).
- Perform a pre-flight calibration check (as per your drone’s manual).
- Ensure the area is clear of obstacles and people.
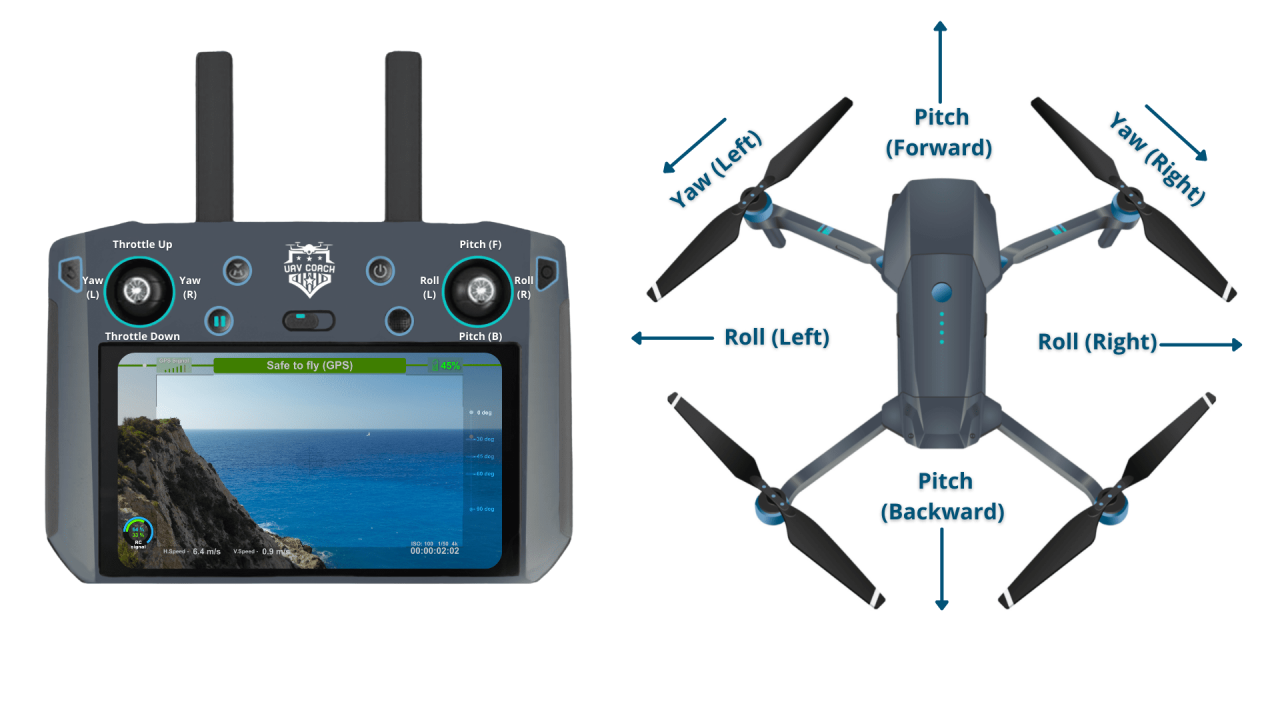
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the basic controls, flight modes, and handling characteristics of various drone types.
Drone Controls
Most drones utilize two control sticks on the remote controller. One stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls forward/backward and left/right movement. Additional buttons control functions like camera settings, return-to-home, and emergency stops. Familiarizing yourself with these controls through practice is essential.
Altitude Hold
Altitude hold is a crucial flight mode that maintains a constant altitude, allowing for more stable and precise flight. This feature significantly reduces the pilot’s workload, especially during aerial photography or videography.
Flight Modes, How to operate a drone
Many drones offer different flight modes to cater to various skill levels and flight situations. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers. Understanding the functionalities of each mode is critical for safe and efficient operation.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control.
- Sport Mode: Allows for higher speeds and more agile maneuvers.
- GPS Mode: Utilizes GPS for precise positioning and return-to-home functionality.
- Attitude Mode: Maintains the drone’s orientation relative to the pilot.
Drone Types and Handling
Different drone types, such as quadcopters and hexacopters, exhibit varying handling characteristics. Quadcopters are commonly used for their maneuverability and affordability, while hexacopters offer increased stability and redundancy in case of motor failure. Understanding these differences allows for informed selection and operation.
Taking Off, Landing, and Basic Maneuvers
Performing safe and controlled takeoffs and landings is crucial for preventing accidents. This section provides step-by-step guides for these maneuvers, along with tips for basic drone control.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
- Ensure the drone is in an open, clear area away from obstacles and people.
- Power on the remote controller and drone, and wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Carefully lift the drone off the ground using the throttle stick.
- Maintain a steady ascent, avoiding jerky movements.
- Once at the desired altitude, hover briefly before commencing other maneuvers.
Controlled Landing Procedure
- Slowly descend the drone using the throttle stick.
- Maintain a steady descent, avoiding jerky movements.
- Once close to the ground, gently lower the drone to a smooth landing.
- Power off the drone and remote controller.
Basic Maneuvers
Basic drone maneuvers include moving forward, backward, sideways, and rotating. Smooth and controlled movements are essential for safe and efficient flight. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area before attempting more complex flights.
Hovering
Hovering involves maintaining a fixed position in the air. This requires precise control of the throttle and directional sticks. Mastering hovering is essential for stable aerial photography and videography.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
This section explores advanced flight techniques such as using GPS coordinates, planning complex flight paths, and aerial photography/videography.
GPS Coordinate Usage
Many drones allow you to input GPS coordinates for precise positioning. This feature is useful for accurately navigating to specific locations and executing pre-planned flight paths. Understanding how to use GPS coordinates enhances precision and efficiency.
Complex Flight Path Planning
Planning and executing complex flight paths requires careful consideration of factors such as obstacles, wind conditions, and battery life. Many drone software applications allow for the creation and execution of pre-programmed flight plans.
Aerial Photography and Videography
Aerial photography and videography require skill and practice. Understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and flight stability are essential for capturing high-quality images and videos.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions presents significant challenges. Strong winds can make it difficult to control the drone, and potentially damage the equipment. Strategies for mitigating wind effects include choosing calmer days, flying in sheltered areas, and utilizing wind resistance techniques.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are crucial for keeping your drone in optimal condition and resolving common issues.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Common malfunctions include low battery warnings, GPS signal loss, motor failures, and gimbal issues. Understanding the potential causes of these problems allows for timely intervention and prevents more serious damage.
Basic Drone Maintenance
- Clean the drone’s body and propellers regularly using a soft cloth.
- Store the drone and batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Inspect the drone for any damage or wear and tear after each flight.
- Properly charge and store batteries to extend their lifespan.
Troubleshooting Tips
Troubleshooting tips for common issues include checking battery levels, restarting the drone and remote controller, and ensuring a strong GPS signal. Consult your drone’s manual for more specific troubleshooting steps.
Troubleshooting Flowchart (Drone Won’t Take Off)
A flowchart visually depicts a step-by-step troubleshooting process. The process starts with identifying the problem (drone won’t take off) and follows a series of checks (battery, GPS signal, propellers, etc.) leading to a solution or a need for professional assistance.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This section Artikels essential legal considerations for safe and compliant drone operation.
Legal Requirements
Legal requirements vary by region and may include registration, licensing, and airspace restrictions. It’s crucial to research and comply with all applicable laws before flying your drone.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of regulations and safe flying practices. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and enhance your skills. Ultimately, proficient drone operation is a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Airspace restrictions and no-fly zones are designated areas where drone operation is prohibited or restricted. These areas may include airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations. Respecting these restrictions is essential for safety and legal compliance.
Prohibited Situations

Drone operation is prohibited in several situations, including flying near emergency responders, operating at night without proper lighting, and flying over crowds or private property without permission. Understanding these restrictions is critical for responsible operation.
Resources for Regulations
Numerous resources provide information on drone regulations, including government websites, aviation authorities, and drone industry associations. Consulting these resources is crucial for staying informed about current laws and obtaining necessary permits.
Drone Photography and Videography Techniques
This section covers techniques for capturing high-quality aerial photography and videography.
Principles of Composition
Aerial photography benefits from strong compositional principles, including the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry. Understanding these principles enhances the visual appeal of your images.
Camera Setting Adjustments
Adjusting camera settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for optimal image quality. Understanding how these settings affect exposure and depth of field is essential for capturing professional-looking images and videos.
Capturing Smooth Video Footage
Smooth video footage requires stable flight and proper camera settings. Using features like gimbal stabilization and smooth, controlled movements enhances the quality of your videos.
Drone Camera Feature Comparison
| Camera Feature | Description | Suitability for Shots |
|---|---|---|
| High Resolution Sensor | Captures detailed images | Landscape, architectural photography |
| Wide Angle Lens | Captures a broader field of view | Wide shots, panoramic views |
| Gimbal Stabilization | Reduces camera shake | Smooth video footage, stable shots |
| 4K Video Recording | Records high-resolution video | High-quality video production |
Battery Management and Safety
Proper battery management is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. This section highlights important aspects of battery charging, storage, and handling.
Proper Charging and Storage
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger and follow the charging instructions carefully. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, as this can damage them and potentially cause a fire.
Risks Associated with Damaged Batteries
Damaged or improperly handled drone batteries pose significant risks, including fire, explosion, and chemical burns. Always inspect batteries for damage before use and dispose of damaged batteries properly.
Safe Battery Handling and Disposal
Handle drone batteries with care, avoiding physical damage or short circuits. Dispose of used batteries according to local regulations, as they contain hazardous materials.
Drone Battery Internal Components
A diagram of a drone battery would show the individual battery cells, protection circuitry (PCM), connectors, and possibly a thermal sensor. Each component plays a vital role in the battery’s function and safety. The cells store energy, the PCM manages voltage and current, connectors enable connection to the drone, and the thermal sensor monitors temperature to prevent overheating.
Mastering drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of safe and responsible drone piloting, encompassing pre-flight procedures, flight controls, advanced techniques, and legal compliance. Remember that continuous practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient drone pilot. As you gain experience, you’ll discover the immense potential of drones for both recreational and professional applications.
So, take to the skies responsibly and explore the world from a whole new perspective!
Detailed FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly quadcopters with GPS and beginner modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with features like automatic return-to-home and obstacle avoidance.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass is crucial for accurate flight. It’s recommended to calibrate it before each flight, especially if you’ve moved to a new location or experienced significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (if available) and attempt a controlled landing. Keep a close eye on its position and be prepared to manually control its descent.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires practice and a solid understanding of safety regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical tips and troubleshooting, consult this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and ensure safe and effective operation of your aircraft.
Proper training and adherence to guidelines are paramount when learning how to operate a drone.
Drone battery life varies depending on the model, battery size, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes, but always check your drone’s specifications.
